電鍍Q&A:吊電、滾電、無電解鍍一次說清楚

| Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Rack Plating | Large or irregular parts are hung on racks for precise plating | Furniture hardware, medical devices, motorcycle parts |
| Barrel Plating | Small parts are plated in rotating barrels, ideal for mass production | Screws, nuts, feet caps |
| Electroless Plating | Uses chemical reactions to deposit metal without electric current | PCBs, electronic parts, internal piping |
| Brush Plating | Localized plating using conductive brushes for touch-up | Military, aerospace, repair work |
| Anodizing | Creates protective oxide layer on aluminum through electrolysis | Aluminum frames, lighting fixtures, phone bezels |
| PVD / CVD (Vacuum Plating) | Physical/Chemical vapor deposition in vacuum for decorative or functional coating | Phone casings, kitchen & bath hardware, tools |
| Multi-layer Plating | Combines copper, nickel, chromium for corrosion resistance and aesthetics | Faucets, car trims |
🔹 What is Electroplating?
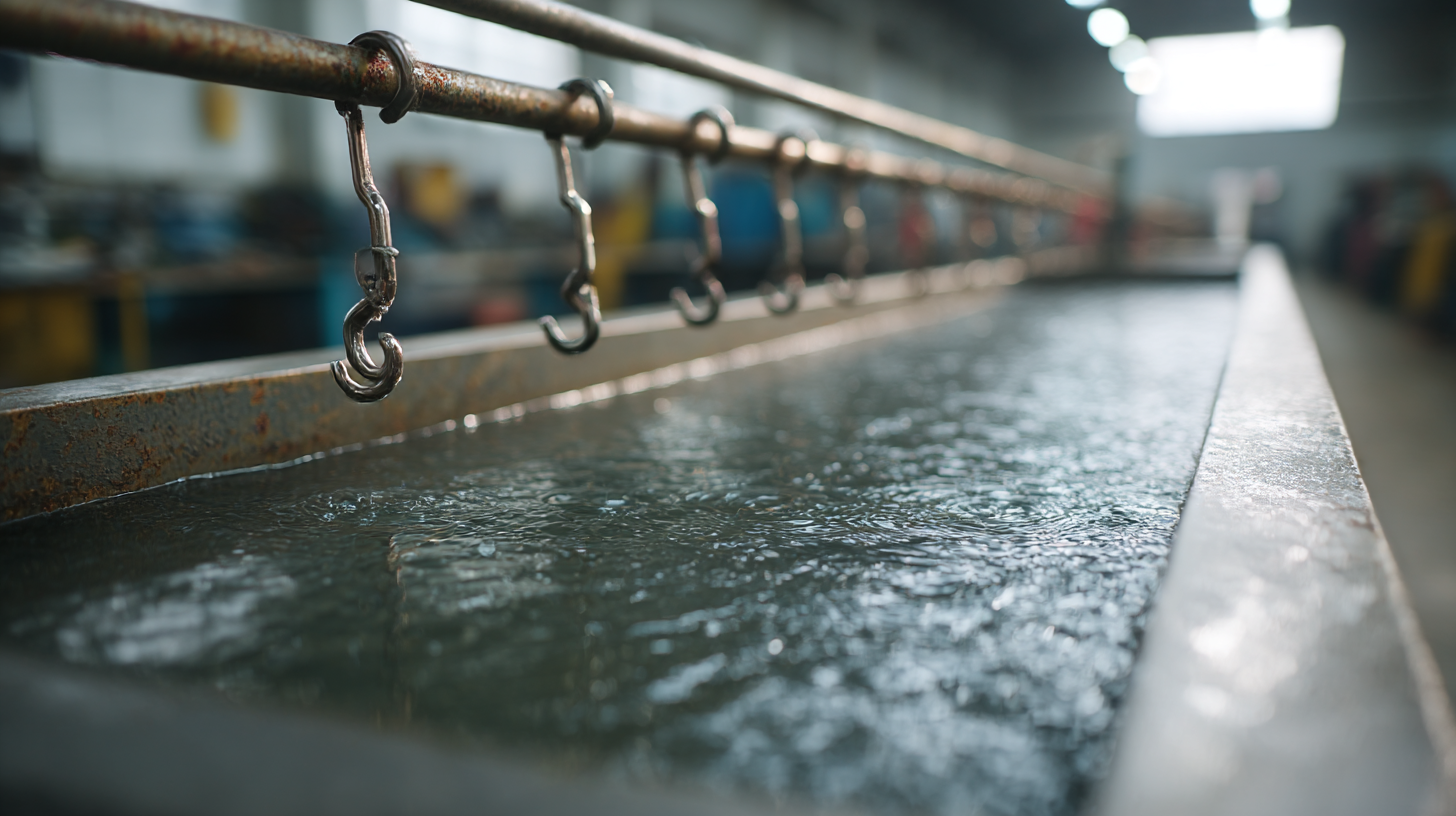
Electroplating is a process where a thin layer of metal is deposited on the surface of a workpiece using electric current. It enhances surface durability, corrosion resistance, and appearance.
🔹 What are the main types of electroplating?
- Rack Plating – For larger, irregular items, offering precise coating.
- Barrel Plating – Ideal for small parts in bulk, such as screws or nuts.
- Brush Plating – Localized repair plating used in aerospace or machinery repair.
- Electroless Plating – No electric current; suitable for electronic parts or piping.
🔹 What metals are commonly used?
Common materials include zinc, nickel, chrome, copper, and gold, depending on required corrosion resistance and visual effect.
🔹 Where is electroplating commonly used?
Electroplating is widely used in hardware parts, automotive components, bathroom and kitchen fittings, and consumer electronics.
🔹 How to choose the right plating method?
Consider part size, batch volume, precision requirements, and aesthetic needs. Contact our technical team for suggestions.